Researchers in Oxford have created a sequence of modular circuit components from hydrogel droplets engineered to selectively transport ions. These ‘iontronic’ devices work collectively seamlessly with residing matter and, in a proof-of-concept demonstration, the workforce designed a natural sensor in a position to measuring the heartbeat of cardiac cell samples.
‘Iontronics is an rising topic that objectives to harness the managed transport of ions as price carriers, analogous to the transfer of electrons in electronics, to course of information and perform computations,’ explains Di Wei, head of the iontronics lab on the Beijing Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems in China. Ion transport already has important functions in vitality utilized sciences like batteries, which often entice or change ions to retailer or discharge vitality. However, the most effective impacts of iontronic devices will in all probability lie of their integration with natural strategies. ‘Should you focus on our private nature, our tissues, the natural language is based on ions – so iontronics could in all probability current a higher interface with cells or tissues,’ explains Yujia Zhang, a bioengineer on the School of Oxford, UK.
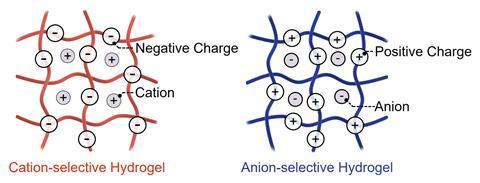
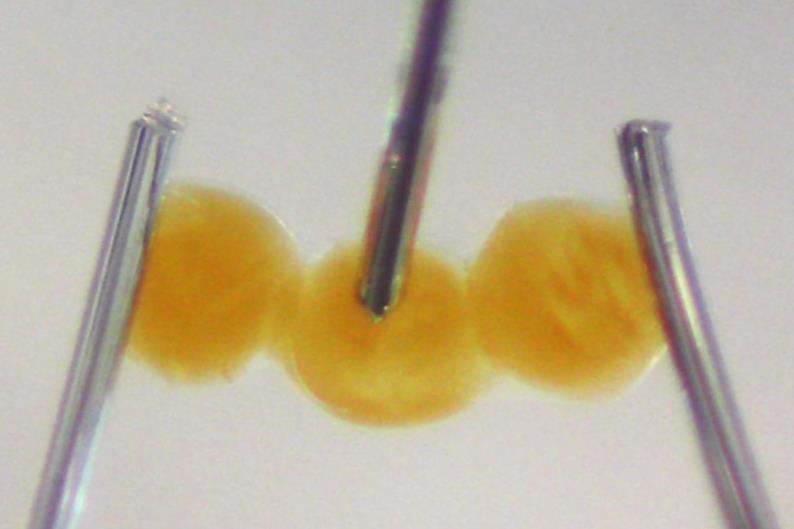
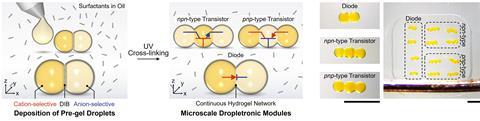
Specializing on this direct natural interface, Zhang and his colleagues developed nano-sized droplets of charge-selective hydrogels that self-assemble into iontronic circuit components along with diodes, transistors, and logic gates. A typical hydrogel is formed of a cross-linked polymer – sometimes derived from a protein – suspended in water, with charged particles able to diffuse all by means of the development. Using a modified silk protein that comes with constructive or unfavourable prices all through the polymer development, Zhang’s workforce created a pair of gels that prohibit this movement of price to each anions or cations. They then deposited specific particular person droplets proper right into a surfactant-containing oil, assembling mixtures of anion- and cation-selective droplets into utterly completely different iontronic components.
‘The following devices carry out by mimicking the behaviour of p- and n-type semiconductors in electronics, with the mobile counterions performing as price carriers,’ explains Wei, who was not involved inside the work. As an illustration, in typical electronics, a diode – a device which ensures current solely flows in a single path – includes a p-type semiconductor adopted by an n-type and is unquestionably replicated by assembling a cation-selective droplet adopted by an anion-selective unit. ‘Because of selective transport of anions and cations on each facet [of the droplet boundary], the overall current path [flows] from the cation-selective facet to the anion-selective facet, resulting in ionic rectification,’ he gives.
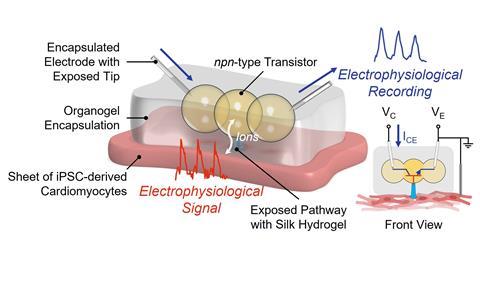
To examine the effectivity of these modular fashions in a natural setting, the workforce created a simple heartbeat monitor by encapsulating an npn-type transistor (containing anion-, cation-, anion-selective droplets) inside an organogel. The machine recorded electrical alerts from samples of atrial and ventricular coronary coronary heart cells, and was even able to distinguish between the two types of cardiac tissue.
There are nonetheless some technical factors to resolve sooner than these devices attain victims, nonetheless Zhang’s workforce is already choices. ‘Iontronic devices often aren’t as extremely efficient as electronics which implies that if we study the output data, we do observe an indication decrease after two or three gates. Moreover, on account of the hydrogel is product of water, it tends to evaporate if we don’t administration the humidity of the surrounding environment,’ he says. ‘We’re now engaged on bettering the effectivity and [trialling] pure gels which may cease that evaporation.’
No matter these challenges, Wei believes this work represents thrilling progress for the sector of iontronics. ‘Using surfactant-supported assembly of hydrogel droplets is a really progressive methodology,’ he says. ‘A standout power is the demonstration of multifunctional capabilities, from diodes and transistors to logic gates and synthetic synapses, all inside a extraordinarily miniaturised and biocompatible system. The worthwhile integration with cardiomyocytes for electrophysiological recording extra highlights the interpretation and potential of this know-how.’