Big-scale, virtually freestanding two-dimensional (2D) gold monolayers, composed of nanostructured patches, have been synthesised using a novel bottom-up technique.
The researchers say that the monolayers, which had been found to have the flexibility to withstand extreme temperatures, may current a useful platform for locating out the catalytic train of 2D gold.
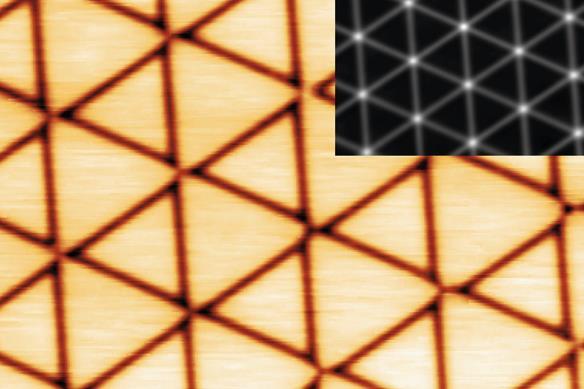
The synthesis of huge, freestanding, single-atom-thick 2D metallic provides stays an issue on account of isotropic nature of metallic bonding. To try to beat this, the researchers developed an technique that involved forming a gold monolayer on an iridium substrate, after which embedding boron atoms on the interface between the gold and iridium. This resulted in suspended monoatomic sheets of gold with a hexagonal building and nanoscale triangular patterns.
Using scanning tunnelling microscopy, x-ray spectroscopies and theoretical calculations they confirmed that the boron interlayer had an vital perform in formation of the nanostructured gold mono- and bilayers, serving to to ensure their stability and structural integrity.
Angle-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy and density purposeful precept revealed {{that a}} decoupling of the gold monolayer from the metallic substrate triggered a transition in its digital properties, reflecting a shift from 3D to mainly 2D metallic bonding.
As a result of the samples had been prepared at comparatively extreme temperatures, they found they’d been thermally regular as a lot as 500°C in vacuum and, with gold comprising the very best layer, may withstand publicity to ambient conditions.
The researchers say their technique not solely advances understanding of the fundamental properties of 2D metals however moreover provides a platform for additional wise analysis. ‘For example, the nanostructured Au motion pictures might facilitate the ordered affiliation of huge molecules or diversified size-selected clusters at a macroscopic scale for added investigations of their catalytic, optical, or magnetic properties,’ they write.