-
Revolutionary drug progress: Targeted protein degradation therapies, which include tagging disease-related proteins for destruction by the proteasome, are rising as a revolutionary methodology in drug progress. This system can objective proteins that standard small-molecule inhibitors can’t, offering new remedy potentialities for various illnesses.
-
Scientific progress: As of 2024, fairly a number of TPD medication are in medical trials, with companies like Arvinas foremost the easiest way. Their breast most cancers drug, vepdegestrant, has achieved a piece 3 medical trial, showcasing the potential of TPD in treating cancers and totally different illnesses.
-
Mechanisms and strategies: TPD depends upon two main strategies: heterobifunctional degraders, which hyperlink a objective protein to an E3 ligase, and molecular glues, which stabilise the interaction between the objective protein and the ligase. Every strategies function to tag the objective protein for degradation by the proteasome.
-
Challenges and enhancements: No matter its promise, TPD faces challenges resembling optimising drug-like properties and determining acceptable objective–ligase pairs. Enhancements like high-throughput screening platforms and new linker designs are serving to to beat these hurdles, paving the easiest way for less complicated and selective TPD therapies.
This summary was generated by AI and checked by a human editor
Definitely considered one of instantly’s hottest pharmaceutical evaluation areas owes quite a bit to alphabetically ordered posters on the 1999 annual Burroughs Wellcome Fund (BWF) college students’ retreat. Though they every had obtained a BWF Junior Faculty Award, Craig Crews and Ray Deshaies hadn’t talked about their work sooner than. Positioned collectively on account of their surnames adopted each other, the pair started an commerce that continued over beer. Crews was studying approaches to hold proteins collectively. Deshaies was studying how E3 ubiquitin ligase enzymes can label proteins to be dispatched for destruction by the cell shredder – the proteasome. ‘I’d really drag in proteins of curiosity and hijack your E3 ligases,’ Crews remembers telling Deshaies.
With colleagues, they demonstrated this targeted protein degradation (TPD) concept in 2001, exploring its potential for a lot of years. In 2008 Crews, at Yale Faculty in New Haven, US, decided to rework this academic concept proper right into a radical new drug modality. Typical small-molecule inhibitor medication typically jam a protein’s carry out like a wrench throughout the gears. Chopping proteins involved in sickness into confetti as a substitute may enable therapies earlier approaches may under no circumstances get hold of. Scientists have discovered larger than 4000 disease-associated proteins, of which current therapies objective spherical 400. The remainder sometimes have troublesome buildings to concentrate on – nevertheless TPD medication could have the power to.
In 2024, many medication using this methodology in the intervening time are in medical testing, says Alessio Ciulli from the Faculty of Dundee throughout the UK: as a minimum 36. Within the meantime immunomodulatory medicine (IMiD) most cancers medication moreover work by inflicting E3 ligases to tag proteins for degradation, researchers have been revealing since in 2010. Regulators accepted top-of-the-line acknowledged IMiD, thalidomide, to cope with the bone marrow most cancers a lot of myeloma in 2006 with out completely understanding the way in which it labored. Ciulli stresses these molecules are a model new class, differentiated by their degradation mechanism. ‘It’s really revolutionising how we consider rising a drug,’ he tells Chemistry World.
Amongst many TPD companies is Arvinas, based mostly by Crews in New Haven, which has in all probability essentially the most superior new drug candidate. A potential breast most cancers drug, vepdegestrant achieved a piece 3 medical trial in November 2024. Arvinas is due to report results in early 2025. However, whereas what Crews and Deshaies outlined at first appears an enticingly straightforward picture, as researchers look additional rigorously into TPD, its complexity solely grows.
Objective, tag, destroy
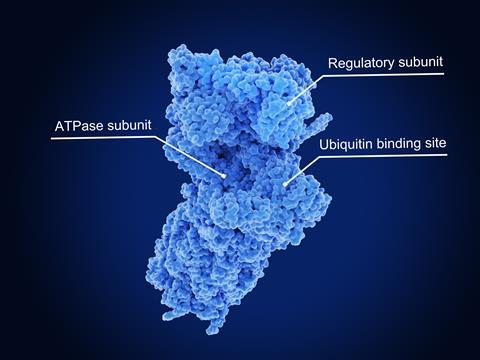
TPD depends upon the tens of tons of of proteasomes already in each of our cells, explains Si-Han Chen from Bristol Myers Squibb in San Diego, US. Each proteasome is a cylindrical protein difficult with a cap unit on one end that recognises ubiquitin proteins, which mark totally different proteins for degradation. An unfoldase enzyme throughout the cap pulls proteins into the cylinder, unfolding them. Contained within the cylinder, there are three types of protease enzyme. Each protease grabs a particular form of amino acid establishing block throughout the moving into protein, sooner than snipping the hyperlink to the next amino acid. The following confetti-like chains are 2–24 amino acids prolonged, Chen stresses, which totally different enzymes break down sooner than making new proteins with them.
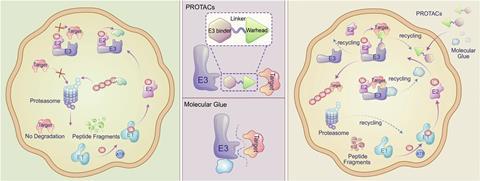
This pure degradation course of is crucial for cell rejuvenation, sustaining protein top quality by eradicating misfolded, damaged proteins from cells, explains Ciulli. The first degraders from Crews and Deshaies used fast amino acid chains, commonly known as peptides, to bind with ubiquitin-adding ligases. Nonetheless peptides don’t enter our cells merely: our our our bodies break apart their amino acids sooner than they get anyplace near a proteasome. So to make medication, Crews needed completely totally different buildings to bind ligases. He labored with Ciulli and others to make additional conventionally drug-like molecules, foremost to some breakthrough papers in 2012 specializing in the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) ligase. ‘This gave confidence early on that we would get to a additional drug-like molecule,’ says Ciulli.
There are two key strategies for hijacking the proteasome to degrade objective proteins, explains Paige Mahaney, chief scientific officer at C4 Therapeutics in Massachusetts, US. In a single approach, heterobivalent degraders like these Crews, Ciulli and colleagues developed have a ligand that binds the protein targeted for degradation at one end, and a ligand for an E3 ligase on the totally different. A linker development connects the two ligands, Mahaney explains. Throughout the totally different approach, molecular glues similar to the IMiDs bind the place objective proteins and ligases meet, stabilising or inducing interactions between them.
‘The potential for TPDs is large and I am excited to see the event of the next-gen degraders,’ says Mahaney. Challenges, nonetheless, embrace optimising drug-like properties and determining acceptable objective–ligase pairs, significantly for molecular glues with shallow binding interfaces.
The recognition in 2010 that IMiDs hijack an E3 ligase ‘was an beautiful validation for’ TPD, says Crews. Such molecular glues are sometimes small drug-like molecules, however their discovery has been serendipitous up to now, says Crews, which limits rational drug progress. Towards this heterobifunctional degraders allow researchers to determine on the ligands at each end, offering a additional rational, targeted and systematic methodology, he supplies.
Thalidomide looms
Allan Jordan, vp of oncology drug discovery at Sygnature Discovery in Nottingham, UK, notes thalidomide’s enormous significance throughout the self-discipline. Nonetheless, it means discovering new patentable molecular glues has been tough, on account of thalidomide and related buildings are so correctly studied. Researchers because of this truth methodology new molecular glues by ‘unbiased screening’. This entails looking out for ligases and proteins that transiently bind, sending the protein for degradation, with out intentionally specializing in each companion. Scientists then show display screen small drug-like molecules, inspecting whether or not or not they extra stabilise the pair. Sygnature presents a platform to help companies do such screening. ‘We are going to then see if any of the degraded proteins are therapeutically viable, and we’re in a position to really do one factor with them,’ Jordan explains.
Roland Hjerpe, senior principal scientist in induced proximity therapeutics at Sygnature, says thalidomide’s small dimension and fascinating physicochemical properties moreover make it a very good ligase-binding ligand for heterobifunctional degraders. Due to this, most heterobifunctionals in medical testing use thalidomide or related buildings, recruiting the ligase it targets, cereblon. Ligands for various ubiquitin ligases, resembling VHL, are larger and fewer helpful for use in medication. Thalidomide is ‘an vital small molecule’, driving enhancements now exhibiting promising results in medical pipelines, Hjerpe says.
Jordan argues thalidomide helped shift the principle goal from peptide-based ligands in heterobifunctional degraders to small molecule ligands. That’s largely on account of cereblon is so promiscuous it ubiquitinates nearly any protein. He remembers a colleague saying at a conference that if degraders hadn’t started specializing in such a versatile ligase then this methodology will not exist the least bit.
Due to this, in heterobifunctional design, medicinal chemists focus on linkers, which administration how ligase and objective proteins align, supplies Hjerpe. That firstly influences whether or not or not the ligases can add ubiquitin tags, he explains. Secondly, linkers moreover affect cooperativity, the place protein–protein interactions help how the ligase and objective protein come collectively. And thirdly, they’re going to enable ‘chameleonicity’ , the place molecules fold as a lot as conceal polar groups with unbalanced distributions of electrons inside fatty buildings the place electrons are additional evenly distributed. Which will improve cell penetration and bioavailability, nevertheless the behaviour is unpredictable. Lastly, medicinal chemists ought to take into consideration how victims’ our our bodies break down the linker, Hjerpe says.
Optimising linkers helps create a gradual interface between the objective protein and the E3 ligase, says Crews. That ought to ensure medication bind additional significantly with the objective protein. And whether or not or not rising molecular glues or heterobifunctionals, proteomics is a needed system in TPD, he supplies. As an example, analysing your full proteome of cells dealt with with drug candidates can assess exactly which proteins are degraded, checking for undesirable potential off-target outcomes.
We’ve been able to degrade nearly all the oncogenic drivers
Ciulli’s employees has been involved in rational TPD drug progress that focuses on stabilising E3 ligase–objective protein interactions. The Dundee researchers captured the first crystal development of a heterobifunctional degrader molecule sure concurrently to every its objective and E3 ligase. ‘We found that stabilising this difficult will enhance the effectivity of ubiquitination, leading to sooner and stronger degradation,’ Ciulli says. ‘If we’re in a position to really see the development of the difficult, we’re in a position to design modifications in a very targeted fashion to truly try and favour recruitment.’
Developing on such data, Ciulli’s lab labored with German drug agency Boehringer Ingelheim to develop prototype degraders for the protein Okay-Ras containing ligands for VHL. Okay-Ras might be essentially the most typically mutated protein in human cancers, the place it tells most cancers cells to develop. Present accepted medication objective just one explicit amino acid mutation, nevertheless TPD can fight many most cancers varieties with totally different Okay-Ras mutations. ‘We’ve been able to degrade nearly all the oncogenic drivers,’ Ciulli says, offering thrilling new potentialities for treating most cancers. Although VHL ligase ligands are a lot much less drug-like, he supplies, as a minimum 4 drug candidates use them.
Rewriting tips
One different key good thing about heterobivalent degraders is that they ‘liberated’ medicinal chemists, says Mahaney. Researchers felt constrained by pointers broadly used to stipulate the buildings of treatment people soak up capsule type, commonly known as Lipinski’s rule of 5, named after their proponent, Pfizer’s Chris Lipinski. Linking ligands for two completely totally different proteins usually presents larger molecules than allowed by the rules. As Lipinski warned, such molecules sometimes don’t dissolve or cross gut cell membranes along with smaller ones. Working in heterobivalent degraders has allowed chemists some freedom to maneuver previous the rule of 5, Mahaney says. Nonetheless they’ve moreover found many elementary guidelines nonetheless apply, resembling limiting the number of hydrogen bonds potential medication could type.
Drug builders can also use TPD to concentrate on non-enzymatic proteins, resembling transcription parts, regulatory proteins and scaffolding proteins, which had been beforehand considered ‘undruggable’ Crews says. Because the sphere matures, the principle goal is shifting to discovering ligands for such targets, he explains. Researchers are asking if they’re going to objective ‘a nook or cranny on the ground of these undruggable proteins’, says Crews.
Differing TPD design guidelines are already evolving the sphere, argues Hjerpe. TPD medication in medical trials hyperlink beforehand acknowledged protein-binding ligands to E3 ligase ligands. As funding shifts within the path of exploring a lot much less established targets, along with these beforehand untargetable with inhibitors, scientists are looking out for novel buildings to bind them. One occasion is central nervous system (CNS) issues like Alzheimer’s sickness, which entails misfolded proteins like amyloid beta and tau proteins aggregating into plaques and tangles respectively. Such aggregating proteins ‘are troublesome to remove by way of using inhibitors’, Hjerpe says.
Sygnature has because of this truth developed a platform known as Charmed to hurry up heterobifunctional degrader discovery. Charmed makes use of high-throughput chemistry to shortly generate and biologically show display screen heterobifunctional molecules, determining if a objective is degradable and determining lead molecules successfully. Jordan explains that they’ve buildings acknowledged to bind to cereblon or VHL pre-attached to linkers pre-dispensed into plastic 96-well plates. Purchasers carry a ‘warhead’, a chemical development acknowledged to bind to concentrate on proteins. ‘Assuming the chemistry is amenable, we’re in a position to hyperlink these collectively pretty shortly,’ Jordan says. ‘It takes a number of week to generate only a few hundred degraders. We talk about democratising degraders – a way of making points accessible to smaller companies.’
Charmed’s focus on merely two ligases shows one key drawback for TPD. ‘Compounds that bind to each a ligase or to a objective protein are tough to develop,’ suggestions Ingrid Wertz, co-founder and chief govt of Lyterian Therapeutics in San Francisco, US. A key occasion is that no matter important funding in rising good VHL ligands, Arvinas opted for medication incorporating cereblon-recruiting thalidomide analogues as lead candidates for medical trials. ‘The TPD group was surprised,’ Wertz says.
TPD ought to moreover overcome new challenges posed by sudden complexity. As an example, when working at Genentech in San Francisco, US, Wertz and Chen had been surprised to go looking out the strategy was not working as anticipated. They examined molecules purported to degrade bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET) proteins. In some assessments cells had been unexpectedly surviving, no matter BET being absent. ‘I was really confused,’ Chen remembers.
Previous most cancers
Wertz, Chen and colleagues discovered that peptides formed when the proteasome chopped up BET had been killing cells by binding with proteins commonly known as inhibitors of apoptosis. Resistant cells produced fewer such peptides, no matter degrading BET. The sudden mechanism is ‘an additional layer of complexity that now we have now to pay attention to,’ says Chen. It stresses the need to be constructive a TPD drug is working by ‘an acceptable modality’, she supplies. The presence of cell-killing peptides is suitable when treating most cancers, she explains nevertheless not in treating totally different sicknesses resembling irritation or neurodegeneration.
The complexity moreover presents an thrilling different, supplies Wertz. ‘It means that you would be able to design your medication intentionally to each generate these peptides if the target is to promote objective cell dying, or to stay away from producing them if the intent is to promote objective cell survival,’ she says.
Protein degradation sometimes leading to completely totally different natural outcomes than inhibition is a nuance requiring deeper understanding of objective biology and degradation, Mahaney supplies. Success will rely on optimising full drug molecules, as delicate changes significantly affect degradation. ‘I really feel early researchers throughout the TPD self-discipline thought that degradation was easy every chemically and biologically,’ Mahaney suggestions.
It’s moreover harder to utilize cell-based and totally different assessments to predict their pharmacokinetics – how medication switch throughout the physique – in animals and other people. ‘Consequently, we should always do additional experiments in animals,’ Mahaney says. Expert scientists at C4 Therapeutics current the data to type out these challenges, Mahaney continues. Now, their pre-clinical outcomes translate correctly to effectivity in medical trials. ‘What’s surprising is how well-behaved these molecules are as quickly as they’re optimised,’ she says.
These outcomes present potential for model spanking new remedy approaches for CNS issues and thoughts tumours
TPD isn’t the one drug approach looking for to interrupt down objective proteins. Small molecule selective oestrogen receptor degraders (Serds) change the type of receptors that signal most cancers cells to develop. On this methodology, clinically accepted Serds elacestrant and fulvestrant recruit an E3 ligase known as arkadia or RNF111 that sends the receptors to the proteasome. The current foremost TPD drug, Arvinas’ vepdegestrant, will be looking for to degrade oestrogen receptors.
Vepdegestrant is in trials as a first- and second-line remedy for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast most cancers. In July 2022, Pfizer paid Arvinas $650 million (£530 million) up entrance, plus a $350 million equity funding, to collectively develop it. Arvinas says vepdegestrant is way safer than imlunestrant, a Serd developed by Eli Lilly, moreover shortly to report part 3 trial outcomes. ‘We now have a transparent drug with a very strongly trending medical revenue,’ Arvinas’ chief medical officer Noah Berkowitz suggested the Guggenheim Securities Healthcare Innovation Conference in November 2024.
Mahaney notes that trials growing previous most cancers into areas like immunology and neurology are proving TPD works, exhibiting promising efficacy and durable pharmacokinetics. C4 Therapeutics has developed extraordinarily selective degraders whose CNS-penetrating capability she says is thrilling. Some current significantly larger thoughts publicity than corresponding small molecule inhibitors. ‘These outcomes present potential for model spanking new remedy approaches for CNS issues and thoughts tumours, significantly given the very good selectivity that could be achieved,’ Mahaney says.
Three accepted molecular glue IMiD therapies current TPD permits worthwhile therapies, Mahaney supplies. ‘There was unimaginable progress all through TPD these days based mostly totally on deeper understanding of learn the way to design small molecular weight molecules which will overcome limitations of present therapies,’ she says. ‘Now, a lot of degraders are transferring shortly by medical progress in the direction of regulatory analysis. It’s a very thrilling time for the sphere.’
Andy Extance is a science creator based in Exeter, UK

