Laptop computer simulations of saturated pure molecules being bombarded by high-energy photons and particles have led a worldwide group of researchers to counsel current ideas surrounding how superior unsaturated molecules type in dense interstellar clouds.
As utilized sciences that allow us to look at interstellar media develop, scientists are discovering that further superior pure molecules are surprisingly plentiful in space. ‘These pure molecules are ubiquitous throughout the universe, so wherever you degree your telescope you might even see pure molecules, a couple of of which might be precursors to amino acids or nuclear bases,’ says Felipe Fantuzzi of the School of Kent throughout the UK, who co-led the work. ‘To understand how these molecules that are necessary to life are customary, and the best way they’re delivered to planets, I really feel, is a really highly effective question in astrochemistry,’ he supplies.
Significantly, understanding how unsaturated molecules type in interstellar media is necessary to elucidate the chemical number of molecular clouds similar to Sagittarius B2, a molecular cloud superior found close to the centre of the Milky Method. ‘The carbon–carbon double bond is rife for oxidation mechanisms, so that’s the place you start to see some truly attention-grabbing chemistry and the formation of distinctive purposeful groups,’ says Julia Lehman an skilled in interstellar spectroscopy on the School of Birmingham, UK, who wasn’t involved throughout the evaluation.
Fantuzzi and their co-workers used Born–Oppenheimer molecular dynamics simulations to research how cosmic rays and x-rays that penetrate dense molecular clouds, ionise and fragment saturated molecules into unsaturated merchandise. They focused on 4 key molecules with a extreme diploma of saturation – ethanolamine, propanol, butanenitrile and glycolamide – which might be current in molecular clouds and seen as potential precursors to further superior biomolecules. Whereas Born–Oppenheimer molecular dynamics has been used to verify molecular fragmentation so far, that’s the major time it was utilized to the sphere of astrochemistry. ‘Principally you may be working a classical molecular dynamics simulation, nonetheless for every step of the dynamics, you may be moreover fixing the Schrodinger equation,’ explains Fantuzzi. This technique allowed the researchers to verify the digital building of the radicals customary beneath extreme vitality processes, and from that, they proposed a group of fragmentation routes that favour constructions with the easiest doable number of π bonds.
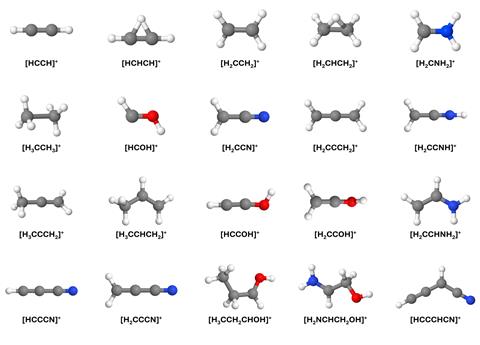
They acknowledged 56 cationic fragments that may be customary from the 4 saturated molecules beneath the extreme vitality circumstances of Sagittarius B2. Most of these fragments comprise a minimal of 1 π bond. Of these unsaturated fragments, 21 have already been seen in interstellar media so the extreme vitality events described on this look at may make clear their formation. Nonetheless, a considerable proportion have not however been detected experimentally and are proposed by the group as potential targets for future investigation by spectroscopists.
‘The researchers have accomplished an excellent job of wanting into one doable route in route of the formation of unsaturated molecules, but it surely absolutely opens up an entire lot of various questions,’ says Lehman. For example, she’d desire to know what reactions occur following the fragmentation and what fragmentation happens beneath lower vitality circumstances. ‘If these molecules are theorised to be there, then now we have to flip spherical and start characterising these throughout the lab so that the observationalists can then detect them.’
